Problema 14-8 Source:
Adapted from Example 3.21 - page 3.24 - SINGH, Ravish -
Book: Network Analysis and Synthesis - 1st edition - Ed. McGraw Hill Education (India) - 2013.
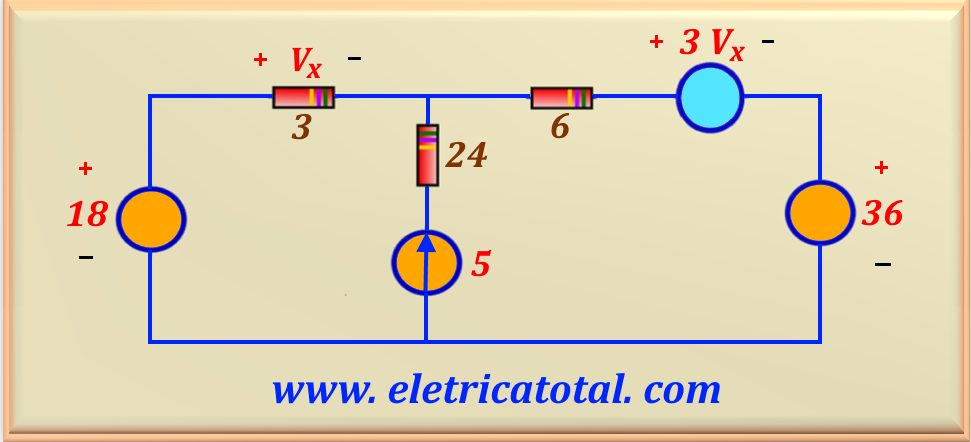
In the circuit shown in Figure 14-08.1 find the value of Vx.
Solution of the Problem 14-8 -
Superposition Method
In the source book from which this problem was taken, the author uses the Superposition theorem for its solution. The solution is very extensive and very likely to miss a signal.
That's why we chose to demonstrate how we can solve this problem quickly and concisely without using the Superposition theorem.
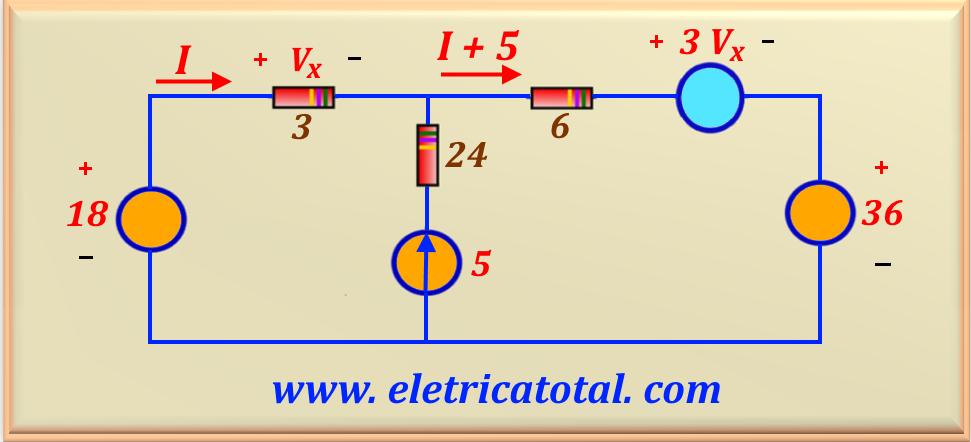
To do so, we will use the circuit shown in Figure 14-08.2.
Note that we call I the current that flows through the 18 V source. Thus, this current also flows through the 3 Ω resistor. Therefore, we can write that:
On the other hand, we see that the current I + 5 flows through the 6 Ω resistor. Therefore, the voltage drop across this resistor is 6 I + 30. As
Vx = 3 I so it is clear that 2 Vx = 6 I . Thus, we can conclude that the voltage drop across the 6 Ω resistor is
2 Vx + 30. So, making the external loop of the circuit we can write:
Solving this equation we find the value of Vx, or:
Therefore, we show that by adopting an alternative technique we drastically reduce the time and the possibility of error in solving the problem.