Problem + Hard 5-2
Source:
exerc.: 26 - section 17.3 - page 727 - - HAYT, William H. Jr. ,
KEMMERLY, Jack E. , DURBIN, Steven M. - Book: Analysis of Circuits in Engineering -
Ed. McGrawHill - 8th Ed. - 2012.
Using Delta-Star transformations for the circuit below, calculate the resistance
equivalent between the points a-b
Solution of the Problem + Hard 5.2
Pay attention to the fact that this problem presents as the main element
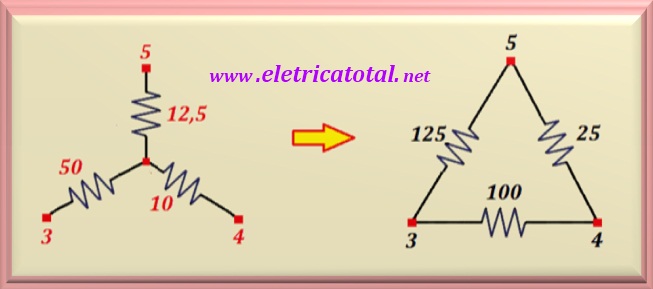
a delta (or triangle) circuit in parallel with a star (or Y) circuit. Soon, the
The first step will be to transform the star circuit into a delta circuit.
In the figure below it is possible to see the transformation that must be carried out. If you want to review the equations
used to carry out these transformations
click here!
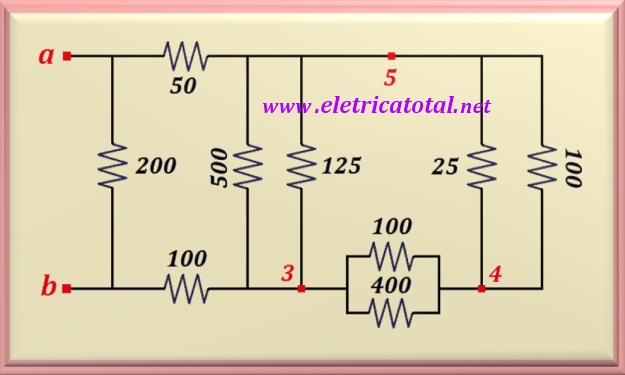
Substituting this new delta circuit into the original circuit, we get the
configuration represented in the figure below, where you can see the two delta circuits in parallel.
Notice that we have a parallel of three sets of two resistors each.
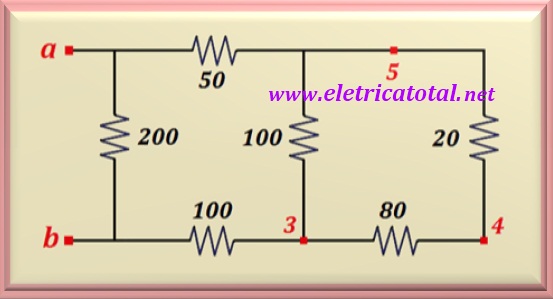
Therefore, solving, we are left with the circuit shown in the figure below.
Note that between points 3 and 5 there are two resistors in series:
one of 20 ohms and the other of 80 ohms. Adding them together, we get 100 ohms
for the equivalent resistance, which
in turn, is in parallel with the other resistor of 100 ohms. Like this,
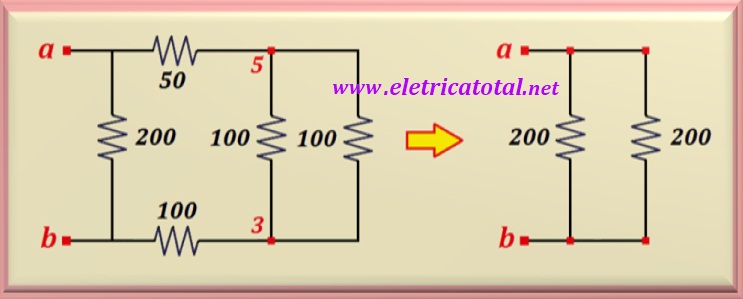
in the figure below, we show how the circuit turned out.
So, between points 3 and 5, with this association, two resistors of 100 ohms appear
each in parallel, which results in an equivalent resistance of 50 ohms.
But this equivalent resistance is in series with the other two (one of
50 ohms and the other 100 ohms), for a total resistance of 200 ohms.
Finally, looking at the right side of the figure, the final circuit that allows
calculate the equivalent resistance between points a and b, that is: